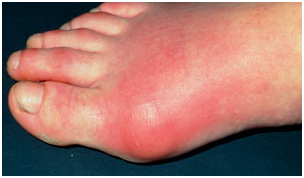
PG NEXT Question of the Day 04-11-2016
The photograph shown below is as a result of disorder of
a. Purine
b. Pyrimidine
c. Glycogen
d. Fatty acid synthesis
Answer : A) Purine
Harper’s illustrated Biochemistry , 30th ed , page 354
GOUT IS A METABOLIC DISORDER OF PURINE CATABOLISM
Various genetic defects in PRPP synthase present clinically as gout. Each defect—for example, an elevated V max, increased affinity for ribose 5-phosphate, or resistance to feedback inhibition—results in overproduction and over excretion of purine catabolites. When serum urate levels exceed the solubility limit, sodium urate crystalizes in soft tissues and joints and causes an inflammatory reaction, gouty arthritis. However, most cases of gout reflect abnormalities in renal handling of uric acid. While purine deficiency states are rare in human subjects, there are numerous genetic disorders of purine catabolism.
Hyperuricemias may be differentiated based on whether patients excrete normal or excessive quantities of total urates. Some hyperuricemias reflect specific enzyme defects. Others are secondary to diseases such as cancer or psoriasis that enhance tissue turnover. Diseases of purine metabolism include Lesch Nyhan syndrome, Von Gierkes Diesease , Hypouricemia , Adenosine deaminase deficiency , purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency.